Abstract
Purpose: Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a life-threatening inflammatory syndrome that may complicate hematologic malignancies (HM). We recently developed a simplified diagnostic and prognostic index termed the 'optimized HLH inflammatory’ (OHI) index comprising the combined elevation of sCD25 (>3,900 U/mL) and ferritin (>1,000 ng/mL) in this context (Zoref-Lorenz A, Murakami J, Hofstetter L, et al. An improved index for diagnosis and mortality prediction in malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood. 2022;139(7):1098-1110). In this study, we assessed whether OHI-positive lymphoma patients have more advanced lymphoma and whether mortality among these patients is related to lymphoma or other causes.
Methods: We performed a multicenter, retrospective study of patients with newly diagnosed lymphoma in whom sCD25 and ferritin levels were measured either as routine surveillance or during investigation for HLH and classified patients by their OHI status. Age at lymphoma diagnosis, complete blood counts, albumin, lactate dehydrogenase, Ann Arbor stage, extranodal site involvement, and ECOG performance status were documented. Overall survival at five years/last follow-up was recorded, as was the cause of death. OHI- and OHI+ patients were compared by international prognostic index (IPI), International Prognostic Score, and Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index for T/B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), Hodgkin's lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma, respectively. Predicted five-year overall survival was calculated based on the relevant prognostic index and was compared between OHI- and OHI+ patients. The odds ratios (ORs) for observed vs. predicted mortality was calculated using the Chi-square test. In addition, time to death by mortality cause analysis was performed.
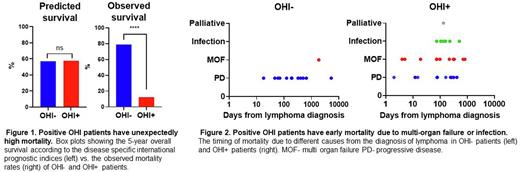
Results: 100 lymphoma patients were studied: 63 were OHI-, and 37 were OHI+, 65% of the patients had B cell NHL, 18% had natural killer/ T cell lymphoma, and 17% had Hodgkin's lymphoma. More than half of the patients had sCD25 and ferritin measured as routine surveillance at the time of malignancy diagnosis (57%). The disease-relevant prognostic index-predicted five-year survival did not differ between OHI- and OHI+ patients (a mean of 57% in OHI- and 58% in OHI+ p=0.62). Compared to OHI- patients, OHI+ patients had a more advanced Ann Arbor stage (p=0.014) but did not differ in the number of extranodal sites, ECOG performance, or disease-relevant IPI. The disease-relevant prognostic index-predicted 5 - year survival did not differ between OHI- and OHI+ patients (Figure 1). However, the actual 5-year survival in OHI+ patients was substantially lower than predicted (12%), reflecting a mortality incidence four times higher than predicted by standard prognostic scoring (OR 3.9; CI 1.3-12.1). By contrast, OHI- patients had better survival (79%) than predicted (Figure 1) by their prognostic scores (OR 0.15; CI 0.07-0.34). In addition, more than half of the OHI+ patients died from non-malignant causes, while most deaths among OHI- patients (92%) were from progressive malignancy. Mortality related to multi-organ failure occurred early in OHI+ patients (Figure 2).
Conclusion: OHI+ patients had a slightly more advanced lymphoma but were generally similar to OHI- patients according to their lymphoma-relevant prognostic index. However, OHI+ patients had a higher mortality rate due to infections and multi-organ failure, suggesting that the OHI index identifies a clinically important inflammatory state in lymphoma patients.
Disclosures
Zoref-Lorenz:Sobi: Consultancy. Iyer:Salarius Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Consultancy. Nikiforow:Kite, a Gilead Compnay: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gurion:Roche: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Medison Ltd: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Raanani:Janssen: Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Daver:Syndax: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Arog: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Servier: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Research Funding; Hanmi: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Trovagene: Research Funding; FATE Therapeutics: Research Funding; Novimmune: Research Funding; Glycometrics: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Trillium: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Shattuck: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy. Ellis:Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gad Medical: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Goyal:Sutro Biopharma: Research Funding; Viracta Therapeutics: Research Funding; SeaGen: Research Funding; UpToDate: Patents & Royalties; 2nd.MD: Consultancy. Jordan:Sobi, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.